BG_crossbridge_TRPN
About this model
This is a bond-graph model of cardiac contraction in the human cardiomyocyte.
- INPUTS:
- Intracellular calcium transient [Ca]i
- OUTPUTS:
- Tension generated by sarcomere
- REACTIONS:
- Re.TRPN_Ca: Binding of Ca to troponin (TRPN)
- Re.BU: Spontaneous switching of crossbridge from B (blocked) to U (unbound) states
- Re.UW: Spontaneous switching of crossbridge from U to W (pre-powerstroke) states
- Re.WS: Spontaneous switching of crossbridge from W to S (powerstroke) states
- Re.SU: Spontaneous switching of crossbridge from S to U states
Model status
The current CellML implementation runs in OpenCOR.
Model overview
This model is based on existing kinetic models, where the mathematics are translated into the bond-graph formalism. This describes the model in energetic terms and forces adherence to the laws of thermodynamics.
For the following bond-graphs, all enzymes are shown in maroon. A '0' node refers to a junction where all chemical potentials are the same. A '1' node refers to all fluxes being the same going in and out of the junction.
| Abbreviation | Name |
|---|---|
| Cai | Calcium, intracellular |
| TRPN | troponin C |
| B | Crossbridge in blocked state |
| U | Crossbridge in unbound state |
| W | Crossbridge in pre-powerstroke state |
| S | Crossbridge in powerstroke state |
| λ | Extension ratio of sarcomere |
| Cd | Sarcomere strain of passive component |
| ζx | Distortion in state x |
| T | Tension |
| Ta | Active tension |
| Fd | Passive tension |
| Tref | Maximal active tension at resting length |
| Ttotal | Total tension |
Biochemical reactions
For reaction TRPN_Ca, the rate of Ca unbinding from TRPN is tension dependent. The term was fitted with an exponential function, which is then used as a transformer TF in the resultant bond-graph.

Fig. 1. Bond-graph formulation of calcium binding troponin, with the resulting complex participating in the crossbridge cycle with states B (blocked), U (unbound), W( pre-powerstroke), S (powerstroke).
Tension generation
For differential terms involving tension and displacement, a mass-spring-damper system was used to approximate the model in order to enable translation into bond-graph mathematics. Length terms were dimensionalised through the resting sarcomere length SL_0, and quantities of crossbridge units were dimensionalised through the estimated number of myosin binding sites per sarcomere.
Total tension is the sum of passive and active tension components. The total tension is then fed as an input into Re:TRPN_Ca.
Active tension
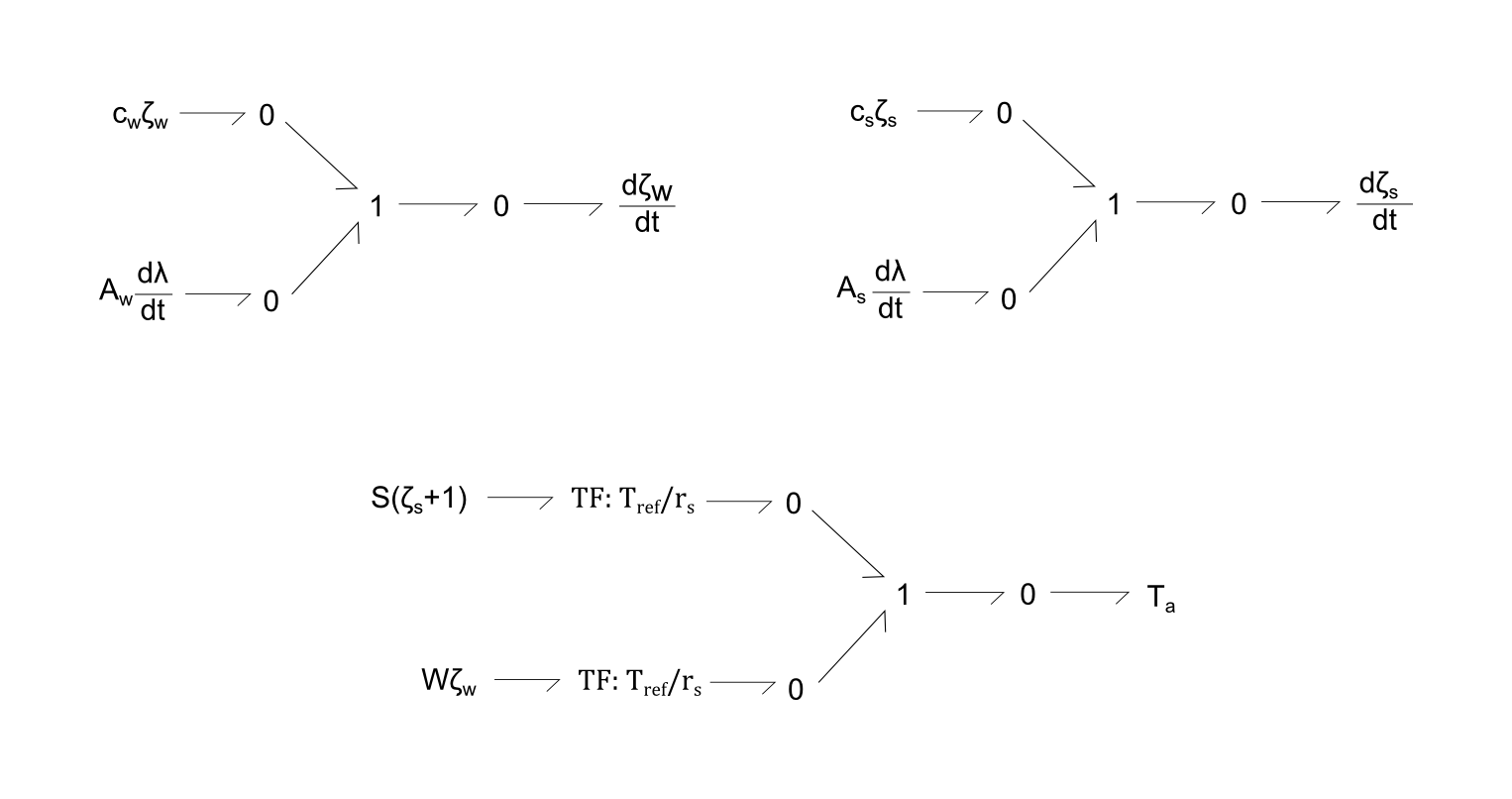
Fig. 2. Bond-graph formulations for distortion states, leading to calculation of active tension (Ta). Each of the three equations are modelled as a 1 node, with sum of potentials of the bonds equalling zero.
Passive tension
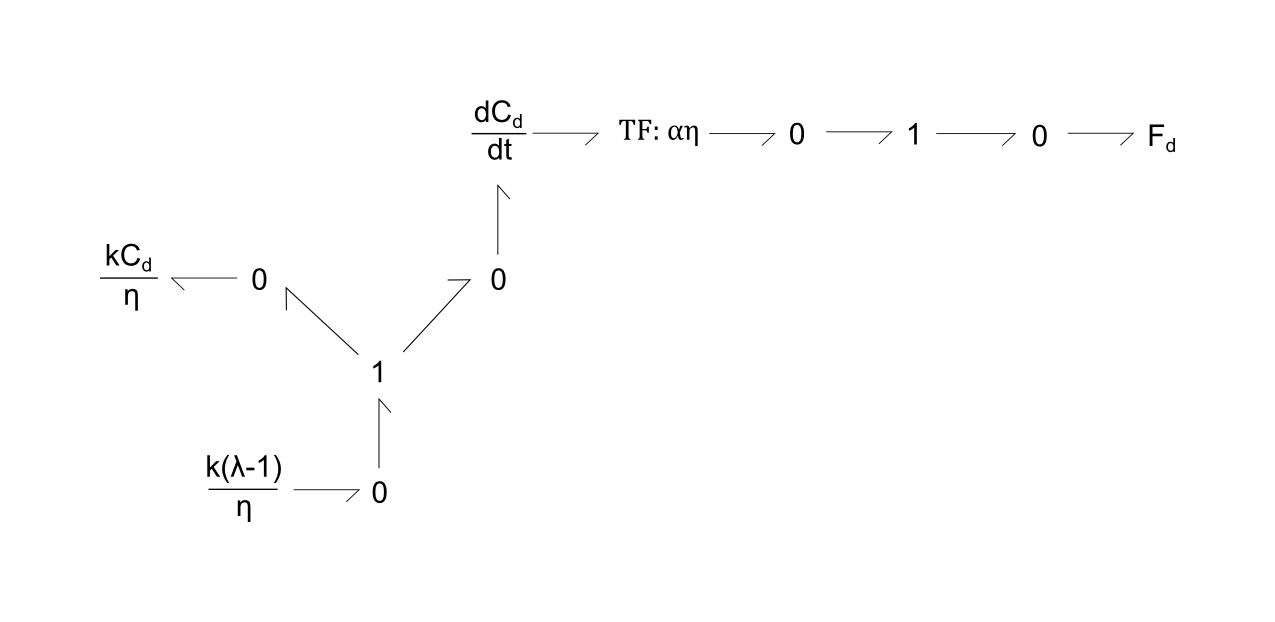
Fig. 3. Bond-graph formulations of strain and extension contributing to passive tension (Fd). Each of the three equations are modelled as a 1 node, with sum of potentials of the bonds equalling zero.
Total tension
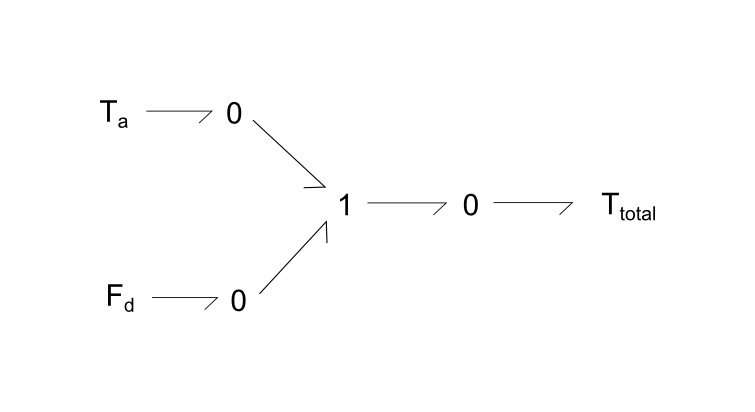
Fig. 4. Sum of active and passive tensions form total tension.
Parameter finding
A description of the process to find bond-graph parameters is shown in the folder parameter_finder, which relies on the:
- stoichiometry of system
- kinetic constants for forward/reverse reactions
- If not already, all reactions are made reversible by assigning a small value to the reverse direction.
Here, this solve process is performed in Python.
Original kinetic model
Land et al: A model of cardiac contraction based on novel measurements of tension development in human cardiomyocytes
Additional detail on the binding of TRPN to Ca was taken from Niederer et al: A quantitative analysis of cardiac myocyte relaxation: a simulation study
